Submit feedback
Can Overload Protection Sockets Prevent Electrical Accidents Effectively?
 2025.12.19
2025.12.19
 Industry News
Industry News
Understanding Electrical Accidents in Everyday Environments
Electrical accidents remain a persistent safety issue in residential, commercial, and light industrial settings. Common incidents include overheating, short circuits, insulation breakdown, and electrical fires caused by excessive current flow. These problems often originate from overloaded wall sockets, where multiple appliances draw more power than the circuit or outlet was designed to handle.
As modern homes and offices rely on power-hungry devices such as heaters, air fryers, servers, and charging stations, traditional sockets without protective mechanisms become vulnerable points. This growing risk has driven attention toward the socket with overload protection as a practical safety upgrade rather than a luxury accessory.
What Is a Socket with Overload Protection?
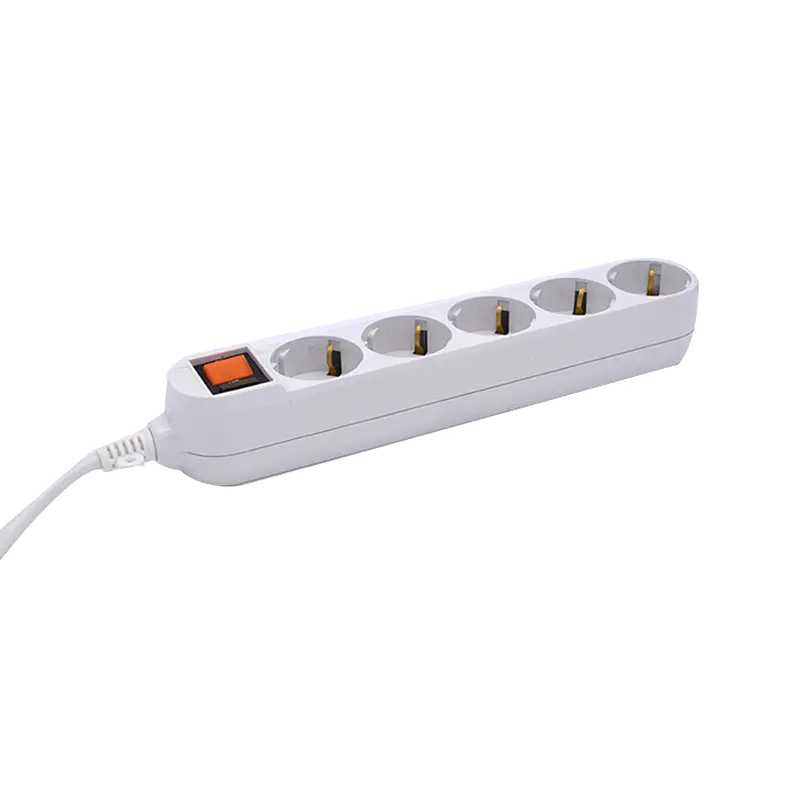
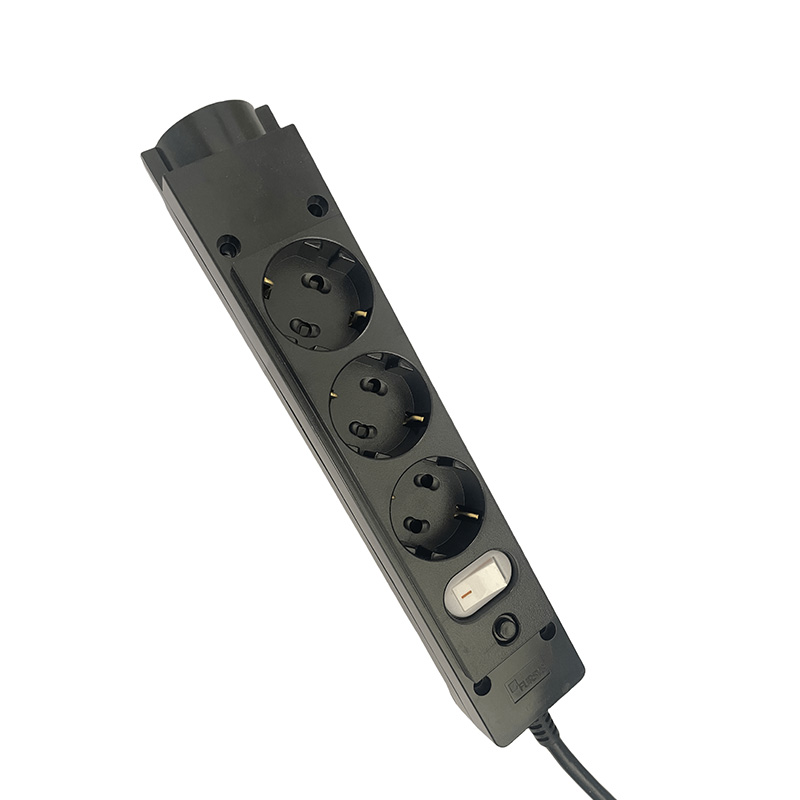
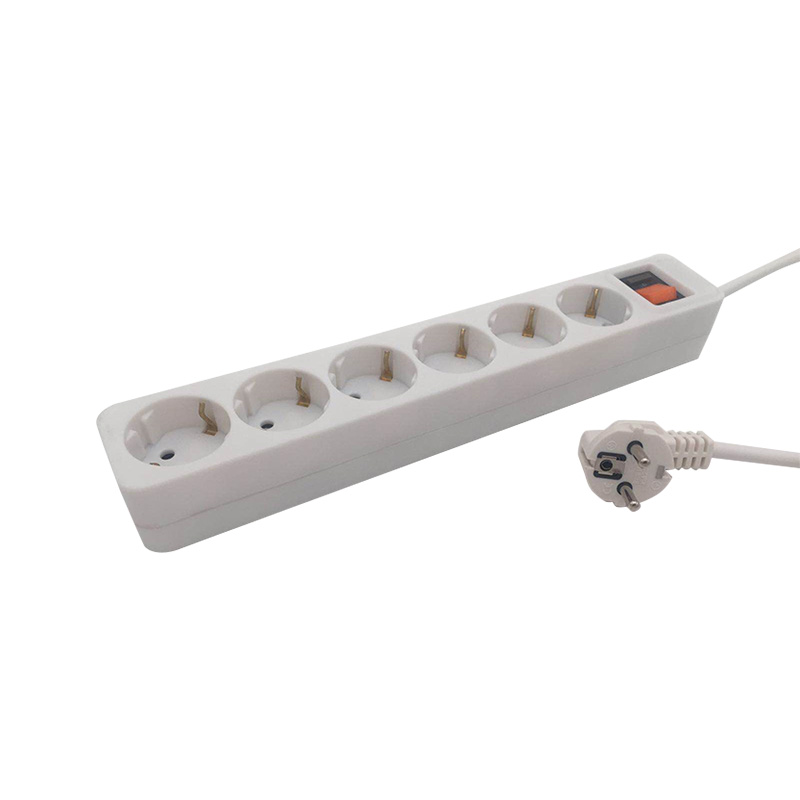
A pc material power strip is designed to automatically interrupt power when the current exceeds a predefined safe threshold. Unlike basic outlets, these sockets integrate internal components that monitor electrical load in real time. When abnormal current levels are detected, the socket disconnects the power supply before wires overheat or components fail.
This protection is typically localized, meaning it responds faster to outlet-level overloads than circuit breakers located in distribution panels. As a result, damage can be prevented at the source, reducing the likelihood of cascading electrical failures throughout the system.
Key Internal Protection Mechanisms
- Thermal cut-off elements that react to excessive heat caused by high current
- Resettable circuit breakers that disconnect and can be manually restored
- Electronic sensors that measure current flow continuously
How Overload Protection Sockets Prevent Electrical Accidents
The primary safety advantage of overload protection sockets lies in early intervention. When too many devices are connected or a single appliance draws excessive power, heat builds rapidly within conductors. If left unchecked, this heat can degrade insulation, ignite nearby materials, or permanently damage equipment.
By cutting off power before temperatures reach dangerous levels, these sockets directly reduce the risk of electrical fires and component failure. This function is especially valuable in older buildings where wiring may not meet modern load demands.
Common Accident Scenarios Addressed
- Overloaded power strips plugged into a single wall outlet
- Continuous operation of high-wattage appliances
- Faulty devices drawing abnormal current
Practical Applications in Homes and Workplaces
In residential settings, overload protection sockets are commonly used in kitchens, living rooms, and home offices. These areas often host multiple devices operating simultaneously, making them high-risk zones for overload conditions. Installing protected sockets in such locations provides localized safety without rewiring the entire electrical system.
In commercial environments, including retail stores and offices, these sockets help safeguard sensitive electronics such as point-of-sale systems, networking equipment, and display units. Even brief overloads can cause costly downtime, which overload protection sockets help prevent.
Comparing Standard Sockets and Overload Protection Sockets
| Feature | Standard Socket | Overload Protection Socket |
| Overcurrent Response | None | Automatic Cut-Off |
| Fire Risk Reduction | Limited | Significant |
| Device Protection | Basic | Enhanced |
Limitations and Misconceptions
While overload protection sockets offer substantial benefits, they are not a complete replacement for proper electrical design. They do not protect against all hazards, such as external power surges caused by lightning or faults upstream in the wiring system. For comprehensive safety, they should be used alongside circuit breakers, surge protectors, and proper grounding.
Another misconception is that overload protection allows unlimited device connections. Users must still respect rated wattage and current limits. The socket’s role is preventive, not permissive.
Are Overload Protection Sockets Worth the Investment?
From a cost-benefit perspective, sockets with overload protection are a practical investment for high-use areas. The marginal increase in upfront cost is often outweighed by reduced fire risk, longer appliance lifespan, and fewer electrical failures. For landlords, businesses, and homeowners alike, these sockets provide an accessible layer of safety without extensive infrastructure changes.
Ultimately, overload protection sockets cannot eliminate all electrical accidents, but they effectively address one of the most common causes: excessive current at the outlet level. When used correctly, they serve as a reliable and proactive safeguard in modern electrical environments.

 TOP
TOP
 ENG
ENG
 English
English русский
русский 한국어
한국어 Deutsch
Deutsch